Market Trends & Demand Evolution
Industry Overview
Profitability & Value Chain Opportunities

*Note: Name, Email and Phone Number are mandatory.
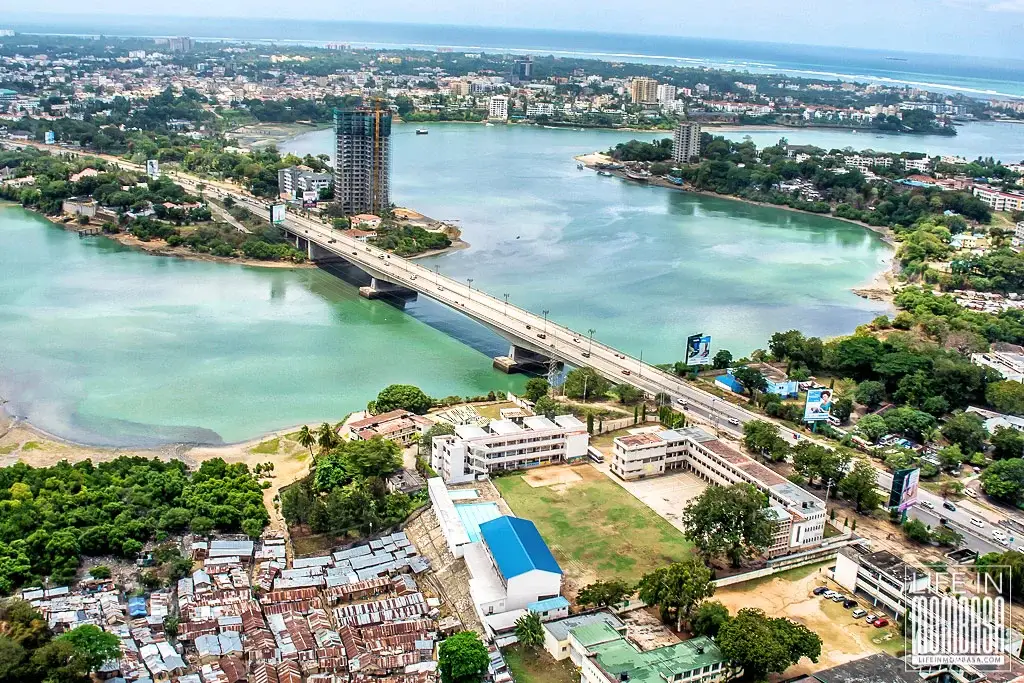


Kenya is one of Africa’s most dynamic investment destinations, strategically located on the eastern coast and serving as a gateway to a regional market of 340+ Mn consumers through the East African Community (EAC).
Kenya holds a leading position in Africa’s renewable energy sectors, with over 70% of electricity generated from renewable sources, geothermal, wind, hydro, and solar. The Port of Mombasa (one of the largest in Africa) strengthens its role as a logistics hub, while Nairobi remains East Africa’s financial and technology centre, home to mobile finance innovations such as M-Pesa.
Area
~580k km²
Capital
Nairobi
Population
~57.7 Mn
Currency
KES
GDP Growth
4.9%
2,770 Km (MGR), 600 Km (SGR)
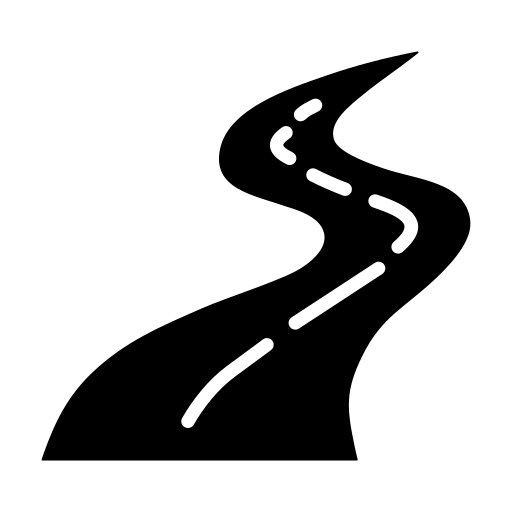

246,000+ Km Road Network
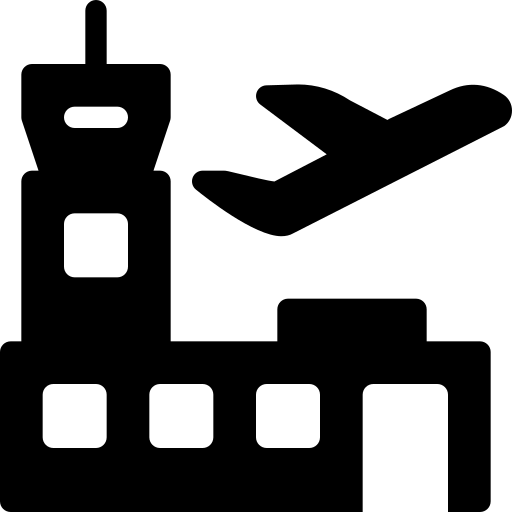

9 International Airports

9 Major Ports
Abundant Natural Resources:
Active Global Investment Destination:
Strong Economic Fundamentals:
Reform-Oriented Government:
Strategic Location-Mombassa:
Textiles

Market Size
$1.84 Bn
CAGR
2.68%
Forecast
$2.05 Bn
Construction Materials

Market Size
$153.94 Bn
CAGR
3.14%
Forecast
$174.05 Bn
Agro Processing

Market Size
$4.59 Tn
CAGR
3.76%
Forecast
$5.52 Tn
Pharmaceuticals

Market Size
$13.66 Bn
CAGR
4.64%
Forecast
$16.38 Bn
FMCG

Market Size
$4.2 Tn
CAGR
2-4%
Forecast
$5.0 Tn
Metals Processing & Refining

Market Size
$508.33 Bn
CAGR
6.60%
Forecast
$847.63 Bn
Automotive & Spares
Market Size
$21.55 Bn
CAGR
5.10%
Forecast
$27.63 Bn
Cassava

Market Size
~$176 Bn
CAGR
4.18%
Forecast
$254.3 Bn
Cotton

Market Size
$6.36 Bn
CAGR
4.91%
Forecast
$8.08 Bn
Groundnut

Market Size
$90.42 Bn
CAGR
2.6%
Forecast
$102.8 Bn
Soya Bean

Market Size
$30.25 Bn
CAGR
4.3%
Forecast
$44.01 Bn
Beverage

Market Size
$1.33 Bn
CAGR
7%
Forecast
$1.74Bn
Meat Processing

Market Size
$163.2 Bn
CAGR
9.96%
Forecast
$261.9 Bn
Palm Oil

Market Size
$8.36 Bn
CAGR
2.6%
Forecast
$10.01 Bn
Sawn Wood

Market Size
$300 Bn
CAGR
4-6%
Forecast
$450 Bn





Jan. 13, 2026
Why Asia is Investing in Africa: 3 Strategic Signals for Global Manufacturers
Market Trends & Demand Evolution
Industry Overview
Profitability & Value Chain Opportunities
Compare
Dear investor, please compare similar category items- either Locations or Opportunities.
*Already subscribed.
*Enter your name/email.

Sign up for exclusive investment alerts.
Already subscribed? Skip
Thank You For Subscribing to
Africa For Investors.

You will be redirected to AFI’s Linkedin Profile in 10 seconds.
Stay On AFI Website